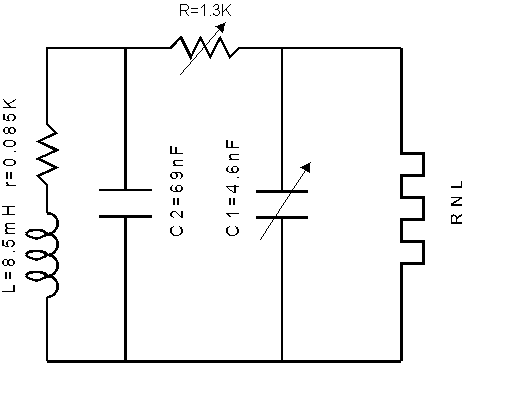
The circuit can be broken down into three parts:
The combined effect of B and C is to give a nonlinear negative resistance of value -R1 for V<Vc and -R1R2/(R2-R1) for V>Vc so that the effective circuit is:

with the current-voltage characteristics of the effective nonlinear resistance given by
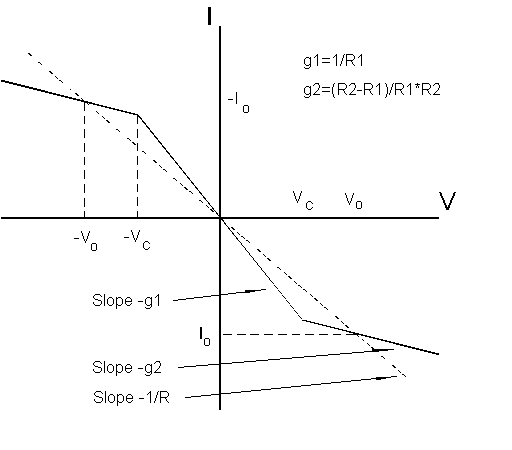
For DC signals the capacitors act as open circuits, and the inductor as a short circuit, so the operating point I0,V0 is given by one of the two intersections of the line of slope -1/R (the load line) with the nonlinear I-V characteristic. (This stationary operating point can be seen by running the applet with C2=75nF for example, when the oscillations gradually decay away.) For suitable values of C1,C2 and L these stationary solutions (fixed points) become unstable to oscillations, and then to chaotic dynamics, first circulating e.g. the I0,V0 fixed point, then switching back and forth between oscillating about the +I0,+V0 and then -I0,-V0 points.